作者 | 崔皓
審校 | 重樓
前陣子,一位運維學員向我傾訴了他的困擾:日常工作中,Prometheus 雖能精準捕捉系統參數異常并告警,但生成的報警信息往往只是冰冷的指標數據。每次遇到異常,他都得手動把這些信息復制粘貼到 DeepSeek 里去詢問分析建議,不僅操作繁瑣,后續也難形成規整的存檔用于技術沉淀。要是能讓報警后自動生成帶分析的智能報表,那該多方便高效啊!
在充分了解他的這一需求后,我給出了一套解決方案 —— 借助 Prometheus Server 與 Alertmanager 的告警機制,再結合 DeepSeek 的 API,讓 AI 自動對告警信息深度分析并生成智能報表。實際驗證下來,這套方案效果很不錯,所以我打算把完整的思路和實驗過程寫成文章,分享給更多同行。
整體思路
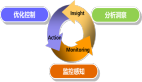
在開始實踐之前,我想先整理一下整體思路,這里我將其分為如下四個步驟,同時也用一張大圖對其進行描述如下:
首先是 “生成指標數據”,它是一切的起點,為后續的監控與分析提供最基礎的 “素材”,這些數據可以是系統的各項運行參數,也可以是業務運行的參數等。
接著進入 “采集數據、異常定義、異常檢測、轉發報警” 環節。系統會采集前期生成的指標數據,同時提前明確什么樣的數據屬于異常情況,之后對數據進行檢測,一旦發現符合異常定義的數據,就會將其轉化為告警并轉發出去。
然后是 “處理報警” 環節,會對接收到的轉發告警進行處理,確保告警信息能被有效承接,為后續的智能分析做好準備。
最后是 “生成智能報告” 環節,借助像 DeepSeek 這樣的 AI 能力,對告警等信息進行深度分析,最終產出更具價值、能夠輔助決策的智能報告。

上面的文字描述了上圖中靠上方的四個實心框體的內容,并且按照箭頭從左到右的順序介紹了整個實踐的執行順序。接著,我們解釋靠下方的四個虛線框,他們會完成具體操作,涉及到服務、代碼、系統以及他們之間的交互。
在整個實踐中,我們需要監控一個應用系統中用戶登陸的情況,當發現登陸異常以后會通過 DeepSeek 分析異常信息,生成異常分析報表,方便我們分析異常以及采取下一步行動。
整個實踐流程環環相扣,按照順序執行。首先,用custom_exporter.py利用 Prometheus Client 的 SDK生成登錄相關指標數據,為后續監控提供基礎。接著,Prometheus 采集這些登錄數據,并提前定義好登錄異常的規則,一旦檢測到異常,就會將告警轉發給Alertmanager。隨后,Alertmanager 接收來自 Prometheus 的告警并進行處理。最后,利用alert_handler.py調用 DeepSeek 大模型,基于告警信息生成智能的異常分析報表,把冰冷的監控數據轉化為更易理解、能輔助決策的智能報告,讓監控從單純的告警通知,升級為具備分析和解讀能力的智能運維工具。
Docker 安裝 Prometheus
在實踐的開始,需要安裝 Prometheus 保證基本的數據采集功能。這里我們采用 Docker 安裝,它能快速且一致地搭建起實驗所需的運行環境。它可將 Prometheus 及其依賴打包成鏡像,讓我們在不同環境下都能便捷部署,無需操心復雜的依賴配置與環境差異問題,同時也便于后續對容器進行管理、版本切換以及遷移等操作。
確保系統安裝 Docker ,在命令行執行如下指令
docker run --name prometheus -d -p 127.0.0.1:9090:9090 prom/prometheus這里對指令稍加解釋如下:
- docker run:創建并啟動容器;
- --name prometheus:指定容器名為prometheus;
- -d:后臺運行容器,不阻塞終端;
- -p 127.0.0.1:9090:9090:將容器內 9090 端口(Prometheus 默認端口)映射到宿主機 127.0.0.1 的 9090 端口,僅允許本地訪問;
- prom/prometheus:使用官方 Prometheus 鏡像,本地無鏡像時會自動從 Docker Hub 拉取。
這里建議大家通過 Docker Desktop 的日志檢查容器是否啟動成功。

當然,此時也可以通過 Web UI 訪問 Prometheus,不過此時還沒有任何數據采集上來。

采集數據
安裝好 Prometheus 之后,我們需要利用它采集指標數據。Prometheus 的設計理念是 “拉取”(Pull)數據,而非 “推送”(Push)。最常用的方式是通過各種 Exporter 將數據以 Prometheus 支持的格式(OpenMetrics)暴露出來,再配置 Prometheus 去拉取。
指標數據(Metrics)
這里需要采集的指標數據,需要做一個簡要說明,在IT監控領域,指標數據(Metrics) 是系統運行狀態和業務活動最核心的量化反映。指標數據的本質包含如下幾個方面:
- 數值化測量:指標是數值(例如:CPU 使用率 75%、每秒處理請求數 1200、過去5分鐘登錄失敗次數 15、當前內存占用 4.2GB)。
- 時間序列:指標數據是按時間順序采集并存儲的一系列數據點。每個點包含一個時間戳(何時采集)和一個指標值(當時的狀態)。
- 核心目的:
- 監控健康狀況:實時了解系統資源(CPU、內存、磁盤、網絡)是否充足,服務是否可用。
- 追蹤性能表現:衡量系統處理能力(吞吐量、請求速率)和響應速度(延遲)。
- 洞察業務行為:記錄用戶活動(如登錄次數、訂單量)、業務流程狀態等。
- 診斷問題根源:當系統異常或性能下降時,指標的變化趨勢和關聯性是定位問題的關鍵線索。
- 支持決策與規劃:基于歷史趨勢預測容量需求,評估優化效果。
簡單來說:指標數據就是將復雜的系統運行情況和業務活動,轉化為可存儲、可計算、可比較、可告警的數字信號,是我們觀察、理解和優化系統的“數據基石”。
關鍵要素預覽:
- 指標名稱 (Metric Name):告訴你測量的是什么(例如:cpu_usage,http_requests_total)。
- 指標值 (Value):具體的測量數值。
- 時間戳 (Timestamp):測量發生的時間點。
- 維度/標簽 (Dimensions/Labels/Tags):(這是理解復雜系統的關鍵!)一組鍵值對,用于細分和豐富指標的含義。例如,一個總的“登錄次數”指標,可以通過標簽細分為“管理員登錄成功次數”、“普通用戶登錄失敗次數”等。標簽讓一個指標能描述無數種具體場景。
本例中,我們讓指標數據 LOGIN_COUNT,用來描述“用戶登錄”的業務行為。定義內容如下:
LOGIN_COUNT = Counter(
'user_login_total', # 指標名稱 (Metric Name)
'用戶登錄總次數及狀態統計', # 指標描述 (Help Text)
['user_type', 'login_status', 'ip_region'] # 標簽/維度 (Labels/Dimensions)
)這里我們對定義的指標進行簡單講解:
1. 指標名稱 (user_login_total):
這是指標的唯一標識符,代表了被測量的是什么。表明這個指標記錄的是“用戶登錄事件”發生的總次數。它是一個 Counter(計數器)。這意味著:
- 它的值只能單調增加(或者重置為0后重新增加)。每次發生一次登錄事件,這個值就會+1。
- 你通常不會直接關注它的絕對值(比如當前值是 12543),而是關注它在一段時間內的變化速率(如:rate(user_login_total[5m])表示過去5分鐘內每秒的平均登錄次數)或一段時間內的增量(如:increase(user_login_total[1h])表示過去1小時內的總登錄次數)。
2. 指標描述 (用戶登錄總次數及狀態統計):
為指標提供人類可讀的解釋,說明這個指標具體測量什么內容。這段描述明確指出,這個計數器統計的是用戶登錄行為發生的總次數,并且會按不同狀態進行統計。
3. 標簽/維度 (['user_type', 'login_status', 'ip_region']):
標簽/維度為指標提供了上下文和細分維度。它們允許你將一個總的登錄次數指標,切割成無數個更細粒度的、具有特定含義的時間序列。
- user_type: 標識登錄用戶的類型。可能的取值示例:"admin","guest"。這個標簽讓你能區分不同類別用戶的登錄行為(例如,管理員登錄次數 vs 普通用戶登錄次數)。
- login_status: 標識登錄嘗試的結果狀態。可能的取值示例:"success","failure"。這是你例子中特別強調的規則用到的標簽。這個標簽讓你能清晰地看到成功登錄、失敗登錄等不同狀態的發生次數(例如,監控登錄失敗率)。
- ip_region: 標識登錄請求來源的地理區域。
安裝 Prometheus Client
在理解了 Prometheus 的數據采集模式(拉取 Pull)和采集的數據內容(指標數據)之后,我們需要在應用或者系統中安裝 prometheus-client 用以數據的生成或者采集。
通過如下命令安裝prometheus-client:
pip install prometheus-client創建 Prometheus Client 應用
完成安裝之后,需要利用prometheus-client 提供的 SDK 生成數據,用來模擬我們要采集的指標數據。在實際操作中可以在用戶目錄(選擇你覺得合適的目錄)下創建一個 Docker 目錄,并在 Docker 目錄下創建 promethues 目錄,接著創建custom_exporter.py 文件。
大致的目錄結構如下圖所示,后面我們會在promethues 目錄下面放入實踐需要的腳本、服務、日志文件等信息。

創建的 custom_exporter.py 文件內容如下:
from prometheus_client import start_http_server, Counter
import random
import time
# 定義一個計數器類型的指標(累計值,適合記錄次數)
# 標簽說明:
# - user_type: 用戶類型(普通用戶/管理員)
# - login_status: 登錄狀態(成功/失敗)
# - ip_region: IP所屬地區(模擬分布式用戶場景)
LOGIN_COUNT = Counter(
'user_login_total', # 指標名(遵循Prometheus命名規范:小寫+下劃線)
'用戶登錄總次數及狀態統計', # 指標描述
['user_type', 'login_status', 'ip_region'] # 標簽(用于多維度篩選)
)
def simulate_login():
"""模擬用戶登錄行為(每3秒產生一次登錄事件)"""
# 模擬用戶類型(70%普通用戶,30%管理員)
user_type = random.choices(['normal', 'admin'], weights=[0.7, 0.3])[0]
# 模擬登錄狀態(90%成功,10%失敗)
login_status = random.choices(['success', 'failed'], weights=[0.9, 0.1])[0]
# 模擬IP地區(國內主要城市)
ip_region = random.choice(['beijing', 'shanghai', 'guangzhou', 'shenzhen', 'hangzhou'])
# 記錄一次登錄事件(計數器+1)
LOGIN_COUNT.labels(
user_type=user_type,
login_status=login_status,
ip_reginotallow=ip_region
).inc() # 每次調用+1
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 啟動HTTP服務,暴露指標在9091端口
start_http_server(9091)
print("用戶登錄監控Exporter運行在 http://localhost:9091/metrics")
# 持續模擬登錄事件
while True:
simulate_login()
time.sleep(3) # 每3秒模擬一次登錄這里我們對上面代碼進行簡單解讀,有這個代碼在后面會因為測試進行修改,所以還會出現,屆時再對修改部分進行進一步解釋。
這段 Python 代碼創建了一個模擬用戶登錄行為的監控數據采集器,它會持續生成登錄事件數據并通過 Prometheus 格式暴露出來。以下是關鍵組件解析:
1. 核心功能:模擬用戶登錄行為
def simulate_login():
# 隨機生成用戶類型(70%普通用戶,30%管理員)
user_type = random.choices(['normal', 'admin'], weights=[0.7, 0.3])[0]
# 隨機生成登錄結果(90%成功,10%失敗)
login_status = random.choices(['success', 'failed'], weights=[0.9, 0.1])[0]
# 隨機選擇IP地區(國內主要城市)
ip_region = random.choice(['beijing', 'shanghai', 'guangzhou', 'shenzhen', 'hangzhou'])
# 記錄登錄事件
LOGIN_COUNT.labels(
user_type=user_type,
login_status=login_status,
ip_reginotallow=ip_region
).inc() # 計數器+1- 每3秒模擬一次用戶登錄事件(通過time.sleep(3)控制)
- 使用隨機數生成器創建真實場景中的用戶行為分布
- 模擬了業務系統中的關鍵維度:用戶身份、操作結果、地理位置
2. 指標定義:多維度登錄計數器
LOGIN_COUNT = Counter(
'user_login_total', # 指標名稱
'用戶登錄總次數及狀態統計', # 指標描述
['user_type', 'login_status', 'ip_region'] # 三維度標簽
)- 類型:Counter(計數器),只增不減
- 名稱:user_login_total(符合Prometheus命名規范)
- 三維度標簽:
A.user_type:區分用戶身份(普通用戶/管理員)
B.login_status:記錄登錄結果(成功/失敗)
C.ip_region:標記用戶地理位置
3. 數據暴露:Prometheus 采集接口
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_http_server(9091) # 啟動指標暴露服務
print("服務運行在 http://localhost:9091/metrics")
while True:
simulate_login()
time.sleep(3)- 啟動 HTTP 服務(端口 9091)
- 通過/metrics端點提供標準 Prometheus 格式數據
- 持續運行,每3秒產生一個新數據點
完成代碼編寫之后,執行custom_exporter.py 文件如下:
python ~/docker/prometheus/custom_exporter.py看到如下結果:
Exporter運行在 http://localhost:9091/metrics說明 customer exporter 開始運行,訪問對應的地址得到如下結果:
# HELP python_gc_objects_collected_total Objects collected during gc
# TYPE python_gc_objects_collected_total counter
python_gc_objects_collected_total{generatinotallow="0"} 255.0
python_gc_objects_collected_total{generatinotallow="1"} 118.0
python_gc_objects_collected_total{generatinotallow="2"} 0.0
# HELP python_gc_objects_uncollectable_total Uncollectable object found during GC
# TYPE python_gc_objects_uncollectable_total counter
python_gc_objects_uncollectable_total{generatinotallow="0"} 0.0
python_gc_objects_uncollectable_total{generatinotallow="1"} 0.0
python_gc_objects_uncollectable_total{generatinotallow="2"} 0.0
# HELP python_gc_collections_total Number of times this generation was collected
# TYPE python_gc_collections_total counter
python_gc_collections_total{generatinotallow="0"} 40.0
python_gc_collections_total{generatinotallow="1"} 3.0
python_gc_collections_total{generatinotallow="2"} 0.0
# HELP python_info Python platform information
# TYPE python_info gauge
python_info{implementatinotallow="CPython",major="3",minor="9",patchlevel="18",versinotallow="3.9.18"} 1.0
# HELP my_custom_metric 自定義測試指標
# TYPE my_custom_metric gauge
my_custom_metric{label1="test",label2="normal"} 1.3487897665970805配置 Exproter
雖然此時采集數據的服務已經啟動,但是還需要在prometheus server 端對采集數據的服務進行定義,才能夠拉取對應的指標數據,于是在prometheus目錄下面創建 prometheus.yml 文件,如下:
global:
scrape_interval: 5s # 每15秒拉取一次數據
scrape_configs:
# 監控Prometheus自身
- job_name: 'prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']
# 監控本地的自定義Exporter(關鍵配置)
- job_name: 'custom_exporter'
static_configs:
# 這里的IP不是localhost,而是你本地機器的實際IP(容器內訪問宿主機的地址)
# 如何獲取:在本地終端執行 `ifconfig` 或 `ip addr` 查看(例如192.168.x.x)
- targets: ['192.168.0.8:9091'] # 你的本地IP + Exporter端口需要注意的是這里設置的 targets 標簽定義的就是 prometheus-client 的 ip 地址和端口,也就是剛才我們編寫的custom_exporter.py 所運行的ip 地址和端口。
接著,讓我們重啟prometheus 服務器,命令如下:
docker stop prometheus
docker rm prometheus然后執行如下命令:
docker run --name prometheus -d -p 127.0.0.1:9090:9090 -v /Users/cuihao/docker/prometheus:/etc/prometheus prom/prometheus --config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml該命令需要注意的是,通過參數 -v /Users/cuihao/docker/prometheus:/etc/prometheus 的配置,將主機目錄作為配置文件存儲,當修改主機上的 prometheus.yml 會直接影響容器內的配置。
查看指標結果
完成上述操作之后,通過訪問http://localhost:9090/query返回到 prometheus server 的 web 界面。
在查詢輸入框中輸入如下命令:
user_login_total此時會得到對應的指標數據:

可以看到從 192.168.0.8:9091 發送的指標數據,包含了用戶的登錄信息。
我們在輸入框中輸入的 user_login_total 實際上是,查詢語言是 PromQL(Prometheus Query Language),它是用來對 Prometheus 采集到的指標數據進行查詢的語言。下面通過它的幾個組成部分的表格給大家展開描述:
概念 | 說明 | 示例 |
指標名 | 要查詢的基礎指標 | user_login_total |
標簽過濾 | 用 {} 篩選特定維度 | {user_type="admin"} |
時間范圍 | 用 [時間] 指定范圍 | [5m] 最近5分鐘 |
函數 | 數據處理和計算 | rate() , sum() |
運算符 | 數學和邏輯運算 | > , + , / |
聚合 | 按維度分組統計 | by (ip_region) |
因此,我們可以通過編寫 ProQL 按照條件查詢指標數據,后面在設置告警規則的時候會用到。
到這里,我們已經能夠通過 promeheus-client 采集到數據,并且通過 prometheus-server 端的 ProQL 查詢數據結果了。
定義 Prometheus 告警規則
接著,我們就需要針對采集的數據進行報警,這里需要先設置報警規則,當觸發報警規則時通知 alertmanager 進行后續處理。
1. 創建告警規則文件
在你的本地 Prometheus 配置目錄(/Users/cuihao/docker/prometheus)中,新建一個告警規則文件 alert_rules.yml,內容如下(以 “用戶登錄異常” 為例):
groups:
- name: login_anomaly_rules # 規則組名稱
rules:
# 規則1:5分鐘內登錄失敗率超過20%(可能是攻擊或系統故障)
- alert: HighLoginFailureRate
expr: |
sum(rate(user_login_total{login_status="failed"}[5m]))
/
sum(rate(user_login_total[5m]))
> 0.2 # 失敗率>20%
for: 1m # 持續1分鐘觸發告警
labels:
severity: critical # 告警級別(緊急)
annotations:
summary: "登錄失敗率過高"
description: "過去5分鐘登錄失敗率{{ $value | humanizePercentage }},可能存在異常登錄行為"
# 規則2:管理員賬號1分鐘內登錄失敗次數>5次(可能被暴力破解)
- alert: AdminLoginFailureSpike
expr: |
sum(rate(user_login_total{user_type="admin", login_status="failed"}[1m]))
> 5 # 1分鐘內失敗>5次
for: 30s # 持續30秒觸發
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "管理員登錄失敗次數突增"
description: "管理員賬號1分鐘內登錄失敗{{ $value }}次,可能存在暴力破解風險"2. 讓 Prometheus 加載告警規則
修改你的 prometheus.yml 配置文件,添加告警規則文件的路徑(確保和已有配置合并):
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
rule_files:
- "alert_rules.yml" # 加載剛才創建的告警規則文件
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'custom_exporter'
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.0.16:9091'] # 你的Exporter地址這個告警規則文件定義了一個名為login_anomaly_rules的規則組,包含兩個針對用戶登錄異常行為的監控規則:第一個規則HighLoginFailureRate會檢測系統整體登錄失敗率,當5分鐘內平均失敗率超過20%并持續1分鐘時觸發嚴重級別(critical)告警,提示可能存在系統故障或惡意攻擊;第二個規則AdminLoginFailureSpike專門監控管理員賬號的安全狀態,當檢測到1分鐘內管理員登錄失敗次數超過5次且持續30秒時觸發警告級別(warning)告警,提示可能存在暴力破解嘗試。兩個規則都通過PromQL表達式實時計算指標數據,并在觸發時提供包含具體數值的描述信息。
3. 重啟 Prometheus 使配置生效
docker restart prometheus訪問 Prometheus UI 的 “Alerts” 頁面(http://localhost:9090/alerts),可以看到定義的規則,當異常發生時,規則會從 “Inactive” 變為 “Pending” 再到 “Firing”(觸發狀態)。

部署 Alertmanager 轉發告警
到此, Prometheus 的告警規則已經配置完畢,并且可以通過 Web UI 查看到規則。由于 Prometheus 本身不處理告警轉發,需要用Alertmanager接收 Prometheus 的告警,然后轉發到你的處理服務(后續調用 DeepSeek)。因此,接下來我們需要部署和配置 Alertmanager,并且編寫 處理服務 。
1. 安裝啟動 Alertmanager 容器
執行如下指令,在prometheus 目錄下面創建alertmanager 目錄,該目錄下會存放報警處理的文件。并且通過 docker run 命令啟動alertmanager 的容器服務。
# 先創建Alertmanager配置目錄
mkdir -p /Users/cuihao/docker/prometheus/alertmanager
# 啟動容器(映射9093端口,掛載配置目錄)
docker run --name alertmanager -d -p 127.0.0.1:9093:9093 -v /Users/cuihao/docker/prometheus/alertmanager:/etc/alertmanager prom/alertmanager2. 配置 Alertmanager
在 alertmanager 目錄下創建配置文件 alertmanager.yml,通過對該文件的配置,轉發告警到處理服務。
route:
group_by: ['alertname'] # 按告警名稱分組
group_wait: 10s # 組內等待10秒再發送
group_interval: 10s # 組內間隔10秒發送
repeat_interval: 1h # 重復告警間隔1小時
receiver: 'webhook_handler' # 轉發到名為webhook_handler的接收者
receivers:
- name: 'webhook_handler'
webhook_configs:
- url: 'http://192.168.0.8:5008/alert' # 你的處理服務地址(本地5000端口)
send_resolved: true # 告警解決后也發送通知請注意這里我們定義的服務地址是 http://192.168.0.8:5008/alert, 也就是后續需要創建的處理服務需要工作的地址。也就是需要從 docker 容器alertmanager 去訪問本機的 http://192.168.0.8:5008/alert 服務。
3. 重啟 Alertmanager 生效
更新完配置文件需要重啟alertmanager 的容器實例。
docker restart alertmanager4. 將 Prometheus 和 Alertmanager 加入同一網絡
alertmanager 配置完畢之后,還有一個重要步驟,就是要保證 Prometheus 服務和Alertmanager 服務在同一個網絡中。由于我們的實驗一直使用的 docker 容器進行部署,所以需要通過如下操作進行 docker 的網絡設置。
(1)停止運行中的容器
docker stop prometheus alertmanager(2)創建一個共享網絡(若不存在)
docker network create prometheus-network(網絡名稱可自定義,如monitoring-network,保持統一即可)。
(3)將兩個容器加入同一網絡
# 將Prometheus加入網絡
docker network connect prometheus-network prometheus
# 將Alertmanager加入網絡
docker network connect prometheus-network alertmanager(4)重啟容器,使網絡配置生效
docker start prometheus alertmanager(5)驗證網絡是否生效
進入 Prometheus 容器,測試能否解析alertmanager容器名:
# 進入Prometheus容器
docker exec -it prometheus /bin/sh
# 測試DNS解析(若容器內有nslookup)
nslookup alertmanager
# 若沒有nslookup,用ping測試(能ping通說明解析正常)
ping alertmanager5. 讓 Prometheus 連接 Alertmanager
完成網絡設置之后,我們再回頭到Prometheus 配置告警通知,修改 prometheus.yml,添加 Alertmanager 地址如下:
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
- 'alertmanager:9093'這里的alertmanager:9093 就是Alertmanager 服務所在的地址和端口號。
最后,重啟 Prometheus:
docker restart prometheus編寫 DeepSeek 分析代碼
到這里,我們完成了文章開頭所說的前三步操作,如下圖所示。我們將整體思路做一個回顧,已經完成生成中指標數據,采集數據,處理報警的工作,最后需要“生成智能報告”。

編寫alert_handler.py代碼如下:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import os
import sys
import datetime
import json
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv # 用于加載環境變量
# 初始化Flask應用
app = Flask(__name__)
# 加載環境變量(從.env文件讀取DEEPSEEK_API_KEY)
try:
# 嘗試加載環境變量,并添加日志
load_result = load_dotenv() # 默認讀取當前目錄的.env文件
script_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
env_path = os.path.join(script_dir, ".env")
# 配置日志和報告路徑(使用腳本所在目錄)
error_log = os.path.join(script_dir, "error.log") # 錯誤日志路徑
report_dir = os.path.join(script_dir, "alert_reports") # 分析報告保存目錄
# 記錄環境變量加載情況
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
if load_result:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 成功加載環境變量文件: {env_path}\n")
else:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 未找到環境變量文件,使用系統環境變量: {env_path}\n")
# 確保報告目錄存在
os.makedirs(report_dir, exist_ok=True)
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 報告目錄準備就緒: {report_dir}\n")
except Exception as e:
# 記錄初始化錯誤
error_msg = f"初始化文件系統時出錯: {str(e)}"
print(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}") # 控制臺也輸出,方便調試
# 嘗試寫入錯誤日志
try:
with open("error.log", "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}\n")
except:
pass
raise # 拋出錯誤,終止啟動
def init_deepseek_client():
"""初始化DeepSeek客戶端(兼容OpenAI SDK)"""
try:
# 驗證環境變量
api_key = os.environ.get("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY")
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
if api_key:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 成功獲取DEEPSEEK_API_KEY (部分隱藏): {api_key[:4]}****\n")
else:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 未在環境變量中找到DEEPSEEK_API_KEY\n")
if not api_key:
raise ValueError("未在環境變量中找到DEEPSEEK_API_KEY,請檢查.env文件")
# 初始化客戶端(DeepSeek兼容OpenAI SDK格式)
client = OpenAI(
api_key=api_key,
base_url="https://api.deepseek.com/v1" # DeepSeek API基礎地址
)
# 驗證客戶端連接
try:
# 發送一個簡單的測試請求驗證連接
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "test"}],
max_tokens=1
)
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] DeepSeek客戶端初始化成功,API連接正常\n")
except Exception as e:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] DeepSeek API連接測試失敗: {str(e)}\n")
raise
return client
except Exception as e:
# 記錄初始化錯誤
error_msg = f"DeepSeek客戶端初始化失敗:{str(e)}"
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}\n")
raise # 拋出錯誤,避免服務啟動后無法調用API
# 初始化DeepSeek客戶端(服務啟動時執行)
try:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 開始初始化DeepSeek客戶端...\n")
client = init_deepseek_client()
except Exception as e:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 初始化DeepSeek客戶端失敗,服務無法啟動:{str(e)}\n")
raise
def call_deepseek_analysis(alert_info):
"""調用DeepSeek分析告警信息,返回分析結果和報告路徑"""
try:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 開始處理告警分析...\n")
# 1. 驗證并提取告警關鍵信息
if not isinstance(alert_info, dict):
raise ValueError(f"告警信息格式錯誤,預期字典類型,實際為: {type(alert_info)}")
# 驗證必要字段
required_fields = ["labels", "annotations"]
for field in required_fields:
if field not in alert_info:
raise ValueError(f"告警信息缺少必要字段: {field}")
alert_name = alert_info["labels"].get("alertname", "未知告警")
severity = alert_info["labels"].get("severity", "未知級別")
description = alert_info["annotations"].get("description", "無描述")
start_time = alert_info.get("startsAt", datetime.datetime.now().isoformat())
labels = alert_info["labels"]
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 提取到告警信息 - 名稱: {alert_name}, 級別: {severity}\n")
# 2. 構造提示詞(系統角色+用戶輸入)
system_prompt = """ 你是一名資深運維與安全分析師,擅長分析業務系統異常告警。
請根據提供的登錄監控告警信息,生成結構化分析報告,包含:
1. 告警基本信息(名稱、級別、時間、關鍵標簽)
2. 可能的原因分析(結合業務場景,如攻擊、系統故障、用戶行為異常等)
3. 具體處理建議(分步驟說明,可操作)
4. 預防措施(如何避免類似問題再次發生)
報告風格需專業、簡潔,重點突出。
""" user_prompt = f""" 告警詳細信息如下:
- 告警名稱:{alert_name}
- 嚴重級別:{severity}
- 告警描述:{description}
- 發生時間:{start_time}
- 關聯標簽:{json.dumps(labels, ensure_ascii=False)} # 包含用戶類型、地區等維度
請基于以上信息分析并生成報告。
"""
# 3. 調用DeepSeek模型
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 開始調用DeepSeek API進行分析...\n")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat", # 使用的模型名稱
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt}
],
stream=False,
max_tokens=1000 # 限制最大返回長度
)
# 4. 提取分析結果
if not response.choices or len(response.choices) == 0:
raise ValueError("DeepSeek API返回結果為空")
analysis_content = response.choices[0].message.content
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 成功獲取DeepSeek分析結果,長度: {len(analysis_content)}\n")
# 5. 生成分析報告文件
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
report_filename = f"analysis_{alert_name}_{timestamp}.txt".replace(" ", "_")
report_path = os.path.join(report_dir, report_filename)
with open(report_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"=== 告警分析報告 ===\n")
f.write(f"生成時間:{datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}\n")
f.write(f"告警名稱:{alert_name}\n")
f.write(f"嚴重級別:{severity}\n")
f.write(f"發生時間:{start_time}\n\n")
f.write("=== 分析內容 ===\n")
f.write(analysis_content)
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 分析報告已保存至: {report_path}\n")
return analysis_content, report_path
except Exception as e:
# 記錄調用錯誤
error_msg = f"DeepSeek分析調用失敗:{str(e)}"
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}\n")
return f"分析失敗:{str(e)}", None
@app.route('/alert', methods=['POST'])
def handle_alert():
"""接收Alertmanager的Webhook告警,調用分析并返回結果"""
try:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 收到新的告警請求\n")
# 1. 解析Alertmanager發送的JSON數據
try:
alert_data = request.json
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"解析JSON數據失敗: {str(e)}")
if not alert_data:
return jsonify({"status": "failed", "reason": "未收到有效數據"}), 400
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 成功解析告警數據,包含字段: {', '.join(alert_data.keys())}\n")
# 2. 提取第一個觸發的告警
if not alert_data.get("alerts"):
return jsonify({"status": "failed", "reason": "告警數據中無alerts字段"}), 400
if not isinstance(alert_data["alerts"], list) or len(alert_data["alerts"]) == 0:
return jsonify({"status": "failed", "reason": "alerts字段不是有效的列表或為空"}), 400
first_alert = alert_data["alerts"][0]
alert_name = first_alert['labels'].get('alertname', '未知告警')
print(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 收到告警:{alert_name}") # 控制臺輸出
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 處理第一個告警: {alert_name}\n")
# 3. 調用DeepSeek分析
analysis_content, report_path = call_deepseek_analysis(first_alert)
# 4. 返回結果
return jsonify({
"status": "success",
"analysis": analysis_content,
"report_path": report_path
})
except Exception as e:
# 記錄請求處理錯誤
error_msg = f"告警處理失敗:{str(e)}"
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}\n")
return jsonify({"status": "failed", "reason": str(e)}), 500
# 添加一個健康檢查接口,方便測試服務是否正常運行
@app.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health_check():
try:
return jsonify({
"status": "healthy",
"timestamp": datetime.datetime.now().isoformat(),
"services": {
"deepseek": "initialized" if 'client' in globals() else "not initialized",
"report_dir": report_dir,
"report_dir_writable": os.access(report_dir, os.W_OK)
}
})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({
"status": "unhealthy",
"reason": str(e)
}), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 開始啟動alert_handler服務...\n")
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] 服務將監聽端口: 5008\n")
# 啟動服務(監聽所有IP的5008端口)
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5008, debug=True)
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"服務啟動失敗:{str(e)}"
print(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}")
with open(error_log, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"[{datetime.datetime.now()}] {error_msg}\n")
sys.exit(1)上面這段 Python 代碼構建了一個智能告警分析服務,它通過 Flask 框架接收 Prometheus Alertmanager 發送的告警通知,利用 DeepSeek 大模型進行智能分析并生成專業報告。服務啟動時會從 .env 文件加載 API 密鑰并初始化 DeepSeek 客戶端,在接收到告警后自動提取關鍵信息(如告警名稱、嚴重級別和描述),構造專業提示詞調用 AI 接口進行深度分析,最終生成包含原因診斷、處理建議和預防措施的結構化報告保存到本地目錄。整個流程配備完善的錯誤處理和日志記錄,通過 /health 端點提供實時服務狀態監控,將傳統告警升級為智能診斷系統,幫助運維人員快速定位復雜問題根源。
由于 alertmanager 發送報警信息需要基于 Prometheus 官方報警格式,所以我們需要對寫好的代碼進行測試,如下命令執行代碼:
python alert_handler.py通過命令行測試服務。
curl -X POST "http://localhost:5008/alert" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"version": "4",
"groupKey": "{}:{alertname=\"HighLoginFailureRate\"}",
"status": "firing",
"receiver": "webhook_handler",
"groupLabels": {
"alertname": "HighLoginFailureRate"
},
"commonLabels": {
"alertname": "HighLoginFailureRate",
"severity": "critical"
},
"commonAnnotations": {
"description": "登錄失敗率過高,當前失敗率為30%,超過閾值20%",
"summary": "登錄失敗率異常升高"
},
"externalURL": "http://localhost:9093",
"alerts": [
{
"status": "firing",
"labels": {
"alertname": "HighLoginFailureRate",
"severity": "critical"
},
"annotations": {
"description": "登錄失敗率過高,當前失敗率為30%,超過閾值20%",
"summary": "登錄失敗率異常升高"
},
"startsAt": "2025-08-14T08:30:00.000Z",
"endsAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"generatorURL": "http://localhost:9090/graph?g0.expr=sum(rate(user_login_total%7Blogin_status%3D%22failed%22%7D%5B5m%5D))+%2F+sum(rate(user_login_total%5B5m%5D))+%3E+0.2&g0.tab=1"
}
]
}'測試功能
按以下步驟逐步驗證,每一步確認無誤后再進行下一步:
終端窗口 | 命令(操作) | 作用 |
窗口 1 | 啟動 Exporter(帶控制接口)cd /存放/custom_exporter.py的目錄python custom_exporter.py | 生成模擬登錄數據, 暴露 9091 端口指標, 9092 端口控制接口 |
窗口 2 | 啟動處理服務(alert_handler)cd /存放/alert_handler.py的目錄python alert_handler.py | 監聽 5000 端口, 接收告警并調用 DeepSeek |
窗口 3 | 啟動 Prometheus 容器docker start prometheus | 采集數據、檢測異常 |
窗口 4 | 啟動 Alertmanager 容器docker start alertmanager | 轉發告警到處理服務 |
安裝上述操作之后,觀察如下圖的 alert_reports 目錄,這個目錄下面保存了生成分析報告信息。如下圖所示:

作者介紹
崔皓,51CTO社區編輯,資深架構師,擁有18年的軟件開發和架構經驗,10年分布式架構經驗。